
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterised by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It often begins in early childhood and can persist into adulthood. Eczema requires personalised treatment.
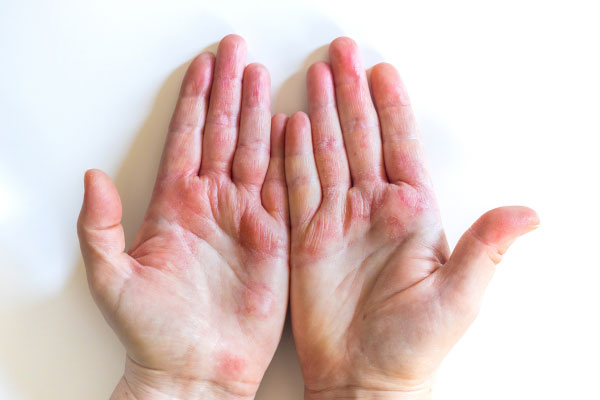

Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a debilitating skin condition due to the severe itch it causes.
Eczema can cause children to be irritable and disrupts their sleep leading to possible delays in learning and development. Most eczema can be effectively controlled with the right treatment and preventative strategies. Some more severe cases require ongoing stronger treatments but in these cases, it can allow the sufferer to reclaim their life.
Despite a known genetic cause, the exact mechanism and factors involved in the formation of eczema are yet to be fully understood. What we do know is that there is a dual problem of skin barrier dysfunction (compromised skin barrier allowing increased penetration of environmental irritants and allergens through the upper layers of the skin) and an excessive immune reaction (causing release of inflammatory mediators in the skin resulting in redness, itch and swelling). This combination acts as a vicious cycle resulting in further breakdown of the skin barrier and worsening of the eczema. The severe itch makes scratching very difficult to resist, further contributing to the broken skin barrier and setting up an itch-scratch-cycle typical in eczema.
There are many other less common forms of eczema or dermatitis.
These include:
Common types of eczema:
Eczema presents as a rough, red, scaly or bumpy rash. When severe it can become weeping and crusted. The most common areas affected are the flexures (inside elbows and behind knees) and the head and neck in children, but eczema commonly affects all other body areas. It is extremely itchy for most people.
Eczema triggers vary among individuals, but common exacerbating factors include:
Treatment varies greatly depending on the type, extent and severity of the eczema and also the age and personal preferences of the patient.
Of utmost importance is avoidance of exacerbating factors and protection of the impaired skin barrier in order to break the inflammatory cycle prevent progression. It is important to understand however that if the inflammation is not also reduced, then this will prevent the skin from being able to completely repair and thus the cycle will continue.
Treatment can be broadly divided into:
Depending on where you’re at in your journey, you can book an appointment with our dermatology practice, or cosmetic practice.
Depending on individual circumstances, treatment options may include:
39 Station Street, Sunbury VIC 3429
Depending on individual circumstances, treatment options may include:
Building 1: 115 O’Shanassy Street, Sunbury VIC 3429
If you’re a new patient, you’ll be invited to attend an initial consult prior to your service to ensure it’s right for you.

See your GP to obtain a referral
Initial consult to discuss
skin concerns and goals
Receive a treatment plan to support your skin health

Expertise

Long Lasting Results

Healthier Skin
